Link Structure Methods for SEO

The link structure is one of the most important factors in SEO because it heavily affects Rankings, PageRank flow, and user experience (UX). Let’s take a look at 4 of the most popular Link Structure methods used today, discuss their advantages and disadvantages, and see how to optimize each method for user experience and SEO.
Before we get into each of the four Link Structure methods, it’s important to point out that, regardless of which method you use, it’s close monitoring of your website’s analytics that really helps you understand what visitors are looking for, the top entry pages, and the worst performing pages of of your website.
Link All Pages to All Pages
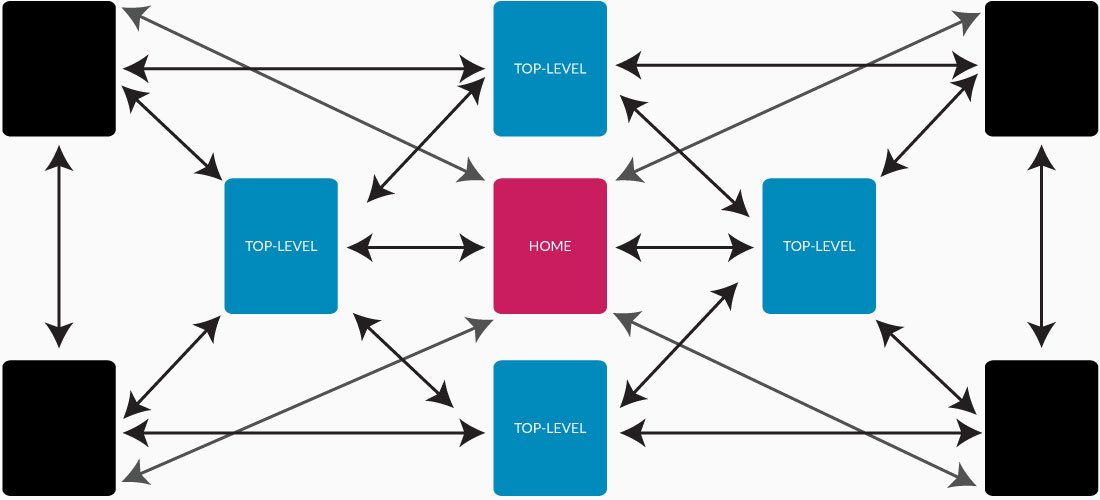
As you may have guessed, every page of this website links to all the other pages. Typically, you’ll see this done when someone uses a massive main navigation with drop-downs and even child drop-downs.
We find this to be by far the least effective technique for any website more than just a few pages. All the hierarchy is gone and PageRank flows freely from your most popular pages to your least (and vice versa).
Trust me. You don’t need your privacy policy page to have the same (or similar) PageRank as your about page.
Deep Link Hierarchy
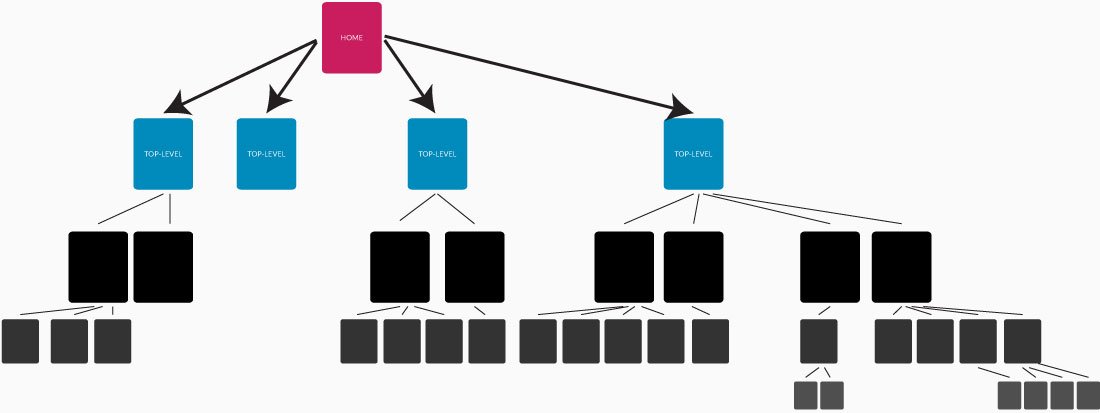
Deep linking is typically only used for VERY large websites or for directories. This method uses a tree-like structure where everything flows from the home page down through progressively more specific pages.
The advantage is that it has a nice clear hierarchy. The problem is that both search engines and users need multiple steps until they land on the page there are looking for. Also, this method can cause indexing problems because there’s bound to be a lot of low-level content duplicated (even if it’s abbreviated) on higher-level pages.
In the end, only the top-level pages see any benefit from this method. The black and grey pages basically fall off the bottom of the SERPs.
Flat Link Hierarchy
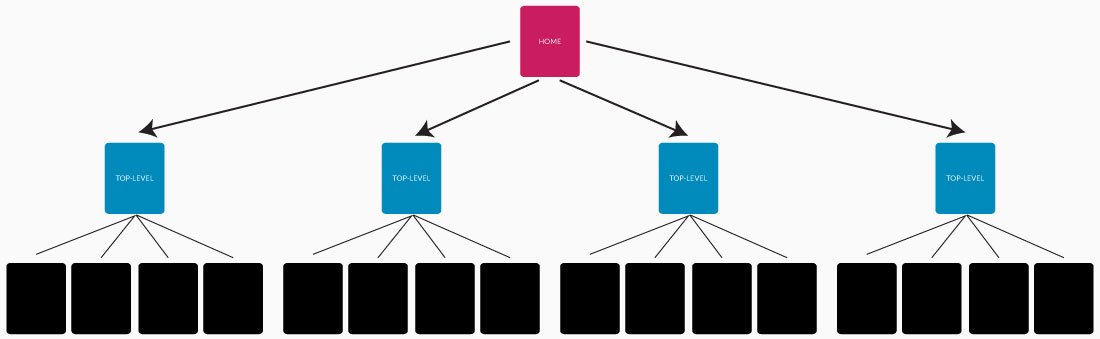
This link hierarchy is the most popular. It’s similar to the tree-like deep linking structure above, but the lower levels are kept as FEW as possible. Thus, the home page links to your top-level “About”, “Services”, “Contact” pages and they may only link to several lower-level pages, but it pretty much stops there.
You will see this most often with marketing websites where the link structure is something like:
- /
- /about/
- /about/bill/
- /about/jane/
- /about/joe/
- /about/susie/
- etc.
There is pretty much nothing allowed to exist below the child of /about/. That helps keeps things as flat as possible And that’s the biggest advantage of a Flat Link Hierarchy. ALL pages of the site are navigable with three clicks or less (theoretically).
Overlapping Link Hierarchy
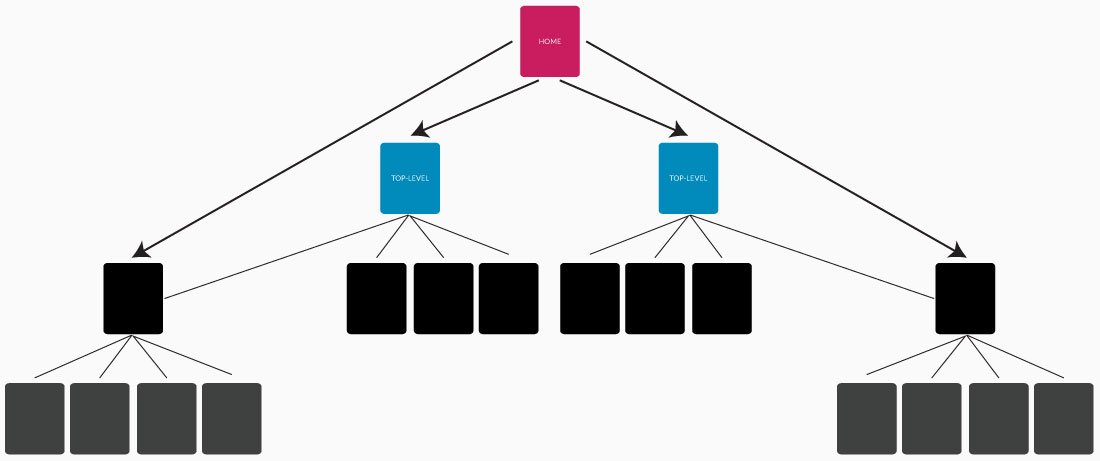
A variation of the Flat Link Hierarchy from above, Overlapping Link Hierarchies are useful for REALLY large websites like directories, forums or eCommerce.
Basically, this hierarchy allows for high-level pages to skip the in-between categories pages and get right to the lower-level stuff. For example, a real estate listing site might want to link to “all houses in Dallas” AND link to “Featured 2-Story Houses in Dallas.”
This method allows you to increase PageRank for your most important category pages as well as improve the indexing of lower-level, but important sub-categories.
Link Structure Methods Summary
Web SEO Analytics published the following comparison table which does a pretty good job of summarizing these 4 techniques.
| Link All pages to All pages | Deep Link Hierarchy | Flat Link Hierarchy | Overlapping Link Hierarchy | |
| PageRank Distribution | All pages get the same amount of link juice | High PageRank on top level pages, low on bottom level pages | Better PageRank distribution compared to Deep Link Hierarchy, variations are used to achieve better results | Good PageRank Distribution |
| Indexing | Poor indexing in large websites, good indexing in small | Poor indexing on the low levels | Some indexing problems are still present on low levels | Fewer indexing problems |
| Navigation | Poor user experience in large websites | Slow navigation, multiple steps to reach low level pages | Fast navigation, in most websites the bottom level pages can be 3 clicks away from homepage | Really fast navigation |
| SEO | Usually internal pages can not achieve high rankings for competitive terms | High rankings for top level pages, low rankings for bottom level | Better Rankings on lower pages compared to Deep Link Hierarchy, variations are used to achieve better results | Better Rankings on lower pages |
Don’t forget to share this article if you like it. Sharing is caring!
Get the Email
Join 1000+ other subscribers. Only 1 digest email per month. We'll never share your address. Unsubscribe anytime. It won't hurt our feelings (much).